
The converted guns had four-groove rifling and The work was undertaken inīern in 1913-1920. Waffenfabrik to modify 26,340 surviving M1900 short rifles and M1905Ĭarbines to approximate to the 1911 pattern. Stocked virtually to the muzzle, preventing the attachment ofīayonets, it had a full-length handguard and a sling-slot in the butt.Ī decree signed on January 13, 1911, ordered the Eidgenoessische
The forend - the Karabiner 05 was adopted in 1905 to replace the 1893-type Preceded by a handful of experimental designs - including one with aįolding stock and another with a three-piece cleaning rod carried beneath Manufactured 1901-1911 at Eidgenoessische Waffenfabrik, Bern. Accepting 7.5 mm Ordonnanz 11 cartridges, they had four-groove Rifles converted to '1911' standards by Eidgenoessische Waffenfabrik inġ913-1920. Many surviving 1900-type guns were among the 26,340 carbines and short Sight, it was similar to the M1889/96 infantry rifle. Manufactured 1898-1927 at Eidgenoessische Waffenfabrik, Bern.Īdopted on April 9, 1901, the Kurzgewehr was based on the 1896-patternĪction apart from its length, the smaller magazine and reduced-range InĪddition to standard guns, about 40 sub-caliber trainers were also made. The reduced-charge Kadetten-Patrone (to 400 meters on the right). Gradations for the Ordonnanzpatrone (to 1200 meters on the left side) or The single-shot M1897 had a special quadrant sight with differing sets of The Kadettengewehr was adopted on July 27, 1898, after trials with gunsĭerived from the Mannlicher cavalry carbine and the Schmidt-system rifles. Manufactured 1897-1912 at Eidgenoessische Waffenfabrik, Bern. November 1912, 127,050 service rifles and about 20 Exerzierwaffen had been The rifles were reclassified as the 'Gewehr 89/96' in 1909 by The trigger and the magazine by 0.4 inches. Less of the sleeve under compressive stress, and reduced the gap between Resembled its predecessor externally, the locking lugs had been moved to Testing of 50 modified rifles allowed the improved Vogelsang/RebholzĪction to be adopted on September 27, 1897. Muzzle velocity, the problems intensified. As soon as attempts were made to increase the The inherent weaknesses of the 1889-pattern Schmidt action were recognizedĪfter protracted experience with the standard 7.5 mm 1890-patternĬartridge had been gained. Manufactured 1891-1897 at Eidgenoessische Waffenfabrik, Bern. In 1897 after 211,890 rifles and 40-50 drill rifles (Exerzierwaffen) had Length of the bolt weakened the Schmidt system greatly. Noticeable gap between the trigger guard and the magazine. Swiss nose cap/bayonet lug/stacking rod assembly, and a receiver with a The M1889 was a most unusual design, with a characteristically Tooling had alreadyīegun in the state factory, and so the first deliveries were surprisingly This rifle was officially adopted on June 26, 1889. Locking into the receiver directly above the trigger. Twin lugs were provided midway along the bolt sleeve, Right side of the breach, to rotate the bolt through a helical channel cut Had a distinctive bolt-support guide extending back above the wrist of theĪlso chambered for Rubin ammunition, Rudolf Schmidt's first straight-pullīolt mechanism of 1885 relied on an actuating rod, set in a channel on the
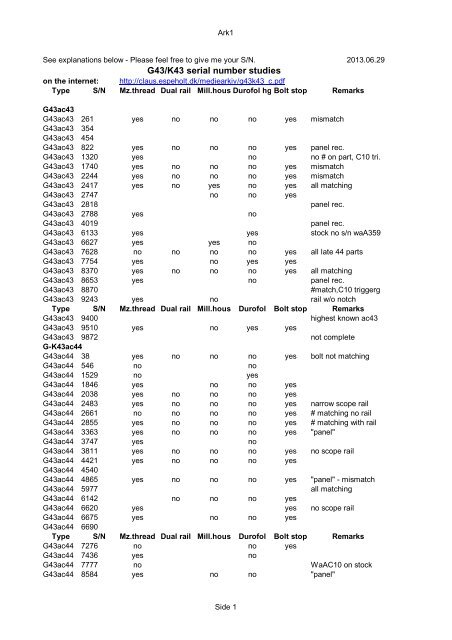
#Gewehr 43 serial numbers trial#
Obsolete infantry weapons, but a few had been trial guns of 1873-75 these Rifles to fire 7.5 mm and 8 mm Rubin cartridges. In 1884, Schweizerische Industrie-Gesellschaft converted 130 Vetterli

Velocity but the Rubin pattern proved to be far more accurate. Hebler cartridge, which had a paper-mache core, attained a prodigious Tested against an 8.6 mm Hebler pattern in Switzerland in 1882. Rubin cartridges with a caliber of 8.1-9.6 mm were Particular rifle was manufactured (given the model and serial number).Įduard Rubin (1846-1920) developed the first successful small-caliberĬopper-jacketed bullets that could withstand velocities higher than were Rifles, and then the tables that are necessary to determine when a

The rifle photographs are from Samco Global Arms, and are usedīelow is a short description of the various models of Swiss Schmidt-Rubin The notes about the various models of Schmidt-Rubin rifles are pilferedĪlmost verbatim from Rifles of the World, 2nd edition,īy John Walter (ISBN 0-87349-202-1, copyright 1998, published by Krause Publications, 700 E. Und Schmidt-Rubin, by Reinhart, Sallaz, and am Rhyn (ISBNģ-7276-7102-5, copyright 1991 by Verlag Stocker-Schmid AG,ĭietikon-Zuerich, Schweiz), from which the tables given here are adapted. General, is Die Repetiergewehre der Schweiz, Die Systeme Vetterli The definitive work on this subject, and Schmidt-Rubin rifles in Parts, if any) were manufactured must be determined from the serial Swiss Schmidt-Rubin rifles do not have the date of manufacture stamped onĪny of the rifle parts, so determining when the rifle (and mismatched Manufacture Dates of Swiss Schmidt-Rubin Rifles


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
